
Emerging Markets for Synthetic Base Stocks
By: Vivek Gupta – National Key Accounts Manager
The lubricants industry is under increasing pressure to deliver peak performance by ensuring machine and system reliability while also meeting stringent environmental, health, and safety standards. As industrial, automotive, aviation, and aerospace technologies continue to evolve, the demand for high-performance lubricants capable of operating under extreme tribological conditions has surged.
Meeting these evolving challenges has been made possible through the use of synthetic base stocks, which play a pivotal role in formulating next-generation lubricants tailored to the emerging needs of these industries.
As environmental regulations become stricter as regulatory requirements for emissions have become more stringent, global markets have progressively adopted advanced technologies and equipment designed to handle higher power densities. Consequently, lubricant formulators have been compelled to develop high-performance lubricants and greases that enhance energy efficiency and ensure greater durability under more demanding conditions leading to the demand for synthetic lubricants and therefore the adoption of synthetic base stocks is accelerating worldwide. Their exceptional ability to perform under extreme temperatures, lower emissions, and boost energy efficiency makes them indispensable for next-generation lubricant formulations.
Synthetic Base Stocks: Driving Performance, Efficiency, and Sustainability in Lubricants
Synthetic base stocks are advanced lubricant fluids formulated to surpass the performance of conventional mineral oils. Produced through chemical synthesis, they offer outstanding thermal stability, excellent oxidation resistance, and precise viscosity control across a wide range of temperatures. Compared to mineral base oils from API Group I to Group III, synthetic base stocks also provide significantly improved low-temperature fluidity and overall durability and some of them add to biodegradability coupled with renewability of carbons, viz., few esters.
The American Petroleum Institute (API) has categorized base oils into five categories as per API 1509. The Group I, II and Group III are derived from petroleum crude oil ,ie, sourced from the refineries. For instance, Group I and Group II base oils are produced in India mainly from refineries of Hindustan Petroleum Corporation, Bharat Petroleum Corporation and Indian Oil Corporation.
Group III base oils are produced by hydrocracking, hydro-isomerization, and hydrotreating, which make this grade more refined. These base stocks are produced from refineries like Neste, S K, S-Oil, ADNOC, GS Caltex, Petronas, etc.
Understanding API Group IV Base Stocks: The Key to Synthetic Lubrication
Synthetic Base Stocks start from API Group IV and are employed to formulate fully synthetic lubricants whether automotive, aerospace, aviation or industrial. They are also used to make speciality greases. API Group IV base stocks consist exclusively of Polyalphaolefins (PAOs).
Polyalphaolefins (PAOs)
Polyalphaolefins (PAOs) are fully synthetic base oils manufactured through a precise polymerization process. They are synthesized from alpha-olefins, mainly 1-decene, which is obtained from ethylene through an oligomerization reaction. Linear alpha-olefins (LAOs) serve as feedstocks for PAOs. In some facilities there are integration of Alpha-Olefins & PAOs production as Ethylene is produced from Ethylene Cracking which acts as the primary feedstock. Further, Oligomerization converts ethylene into linear alpha-olefins, i.e., 1-decene. Alpha-olefins are polymerized into PAOs using metallocene catalysts producing Metallocene PAOs.
Polyalphaolefins are employed for making various high -end synthetic engine oils, gear oils and speciality greases due to their intrinsic unique properties.
Let’s try to decode PAOs by understanding their characteristics and application areas –
Key Characteristics of Group IV Base Stocks (PAOs):
- Fully Synthetic – PAOs are produced via chemical synthesis and lubricants formulated from it are fully synthetic.
- Superior Thermal Stability – PAOs performs well under extremes of temperatures thereby becomes eligible candidates for speciality applications like aviation lubricants, synthetic gear oils, etc.
- Excellent Oxidation Resistance – PAOs extends lubricant life and reduces sludge formation.
- Wide Operating Temperature Range – Due to low pour points and high viscosity indices, can operate at wider temperature zones.
- Low Volatility – Due to their low volatility PAOs can reduce oil consumption in high-temperature applications.
- Superior Lubricity – Reduces friction and wear for enhanced equipment protection.
Common Application areas of Group IV Base Stocks (PAOs):
- Automotive and industrial lubricants
- High-performance engine oils
- Aviation and aerospace lubricants
- Hydraulic and gear oils
- Compressor and turbine oils
Polyalphaolefins (PAOs) are produced by a few specialized manufacturers globally as these companies have expertise in synthetic base stock production and alpha-olefin feedstock processing. Each producer of PAOs has unique production capabilities, technological advancements, and product performance strengths.
PAOs are available in a range of viscosities, starting from as low as 2 cSt for low-viscosity grades and 40 cSt and above for high-viscosity variants. These are commonly referred as Low-Vis PAOs and High-Vis PAOs.
Metallocene Polyalphaolefins (mPAOS)
New advancement in PAOs are Metallocene Polyalphaolefins commonly, referred as mPAOs which represent the next generation of synthetic base oils, offering superior performance compared to conventional PAOs. They are produced using metallocene catalysts, which provide precise molecular control, leading to improved viscosity, oxidation stability, and energy efficiency in lubricants. Metallocene PAOs are revolutionizing synthetic lubricants, providing enhanced durability, efficiency, and sustainability.
Conventional PAOs are typically produced using the Ziegler-Natta polymerization process, whereas mPAOs are synthesized through metallocene catalysts. This advanced method allows for:
- A highly uniform molecular structure, ensuring more predictable and stable lubrication characteristics
- A higher viscosity index (VI), enabling reliable performance across a broad temperature range
- Lower volatility, minimizing evaporation losses even in high-temperature conditions
Metallocene PAOs and Conventional PAOs
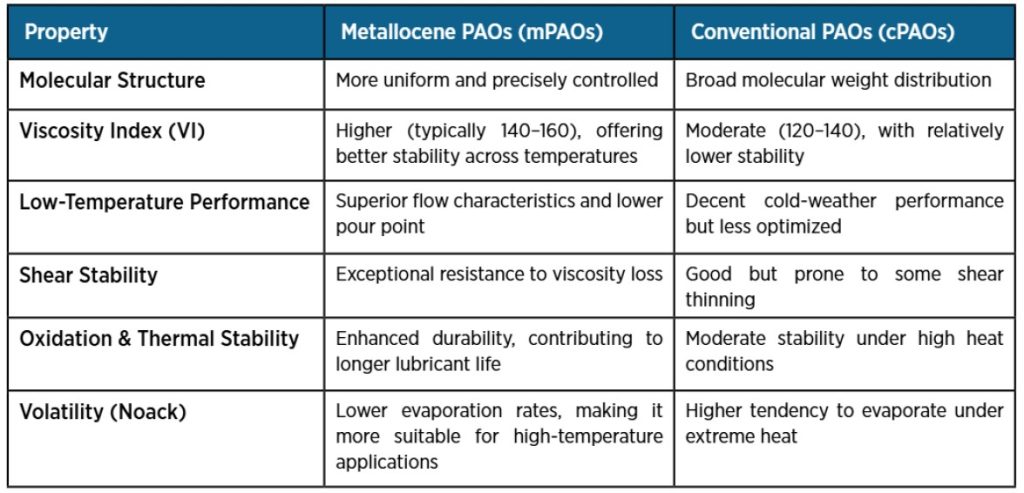
Comparison for Metallocene PAOs vs. Conventional PAOs
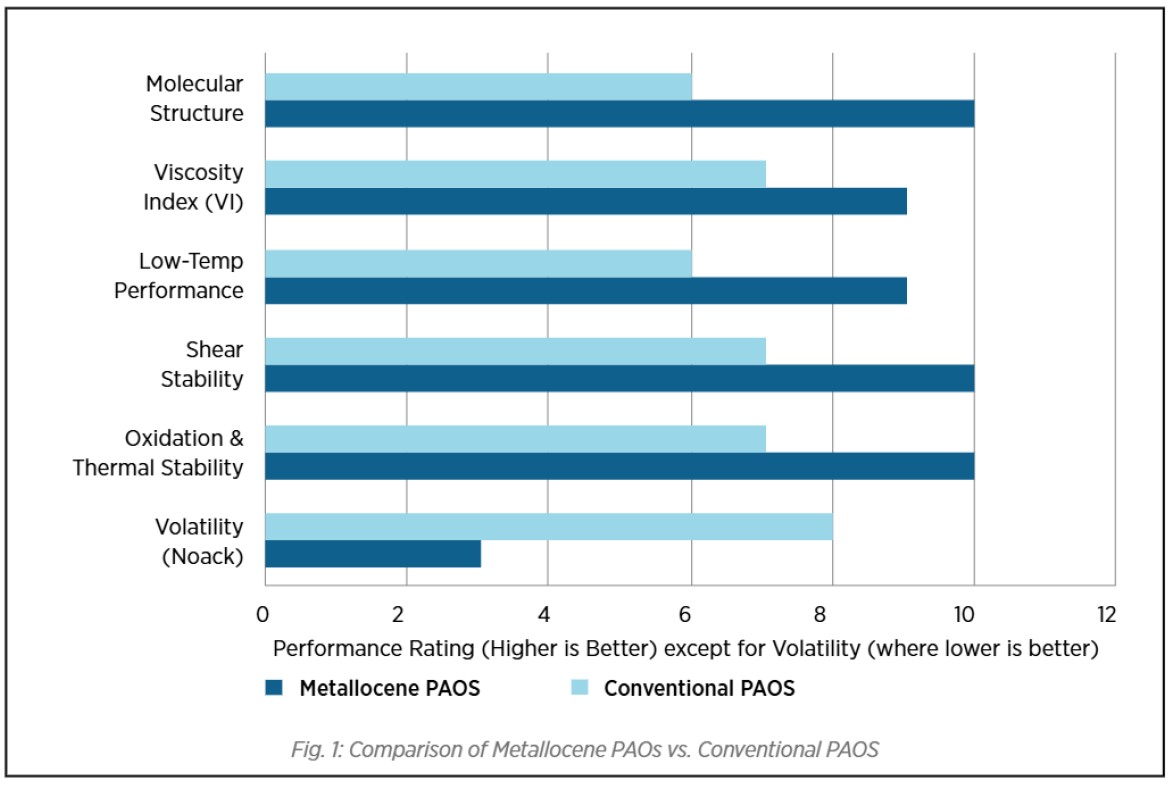
Applications of Metallocene PAOs
- High-Performance Engine Oils
- Used in API Group IV+ synthetic lubricants
- Enhances fuel economy and engine durability
Industrial Gear Oils
- Provides superior wear protection under extreme loads
- Maintains viscosity in high-temperature environments
Aviation & Aerospace Lubricants
- Ensures low volatility and oxidative stability
- Performs well in extreme cold and high-heat conditions
Wind Turbine Lubricants
- Long drain intervals reduce maintenance costs
- Improves efficiency of gearbox operations
Electric Vehicle (EV) Lubricants
- Low friction reduces energy loss in e-mobility systems
- Compatible with high-speed electric motors
Key drivers for metallocene PAOs are growing demand by OEMs for higher fuel efficiencies coupled with long life of lubricants. Another motivating factor for mPAOs are adoption in Electric Vehicles (EVs).
Leading producers of metallocene PAOs include ExxonMobil, Chevron Phillips, INEOS and NACO. These advanced synthetic base stocks are gaining significant traction in the lubricants industry due to their distinct molecular structure and superior performance attributes. Notably, their excellent low-temperature fluidity, shear stability, and minimal volatility at high temperatures (low Noack volatility) make them highly suitable for high-performance lubricants across multiple sectors. Key applications include aerospace, aviation, automotive (particularly long-drain and fuel-efficient engine oils), and industrial operations such as windmills, mining, steel, and cement production.
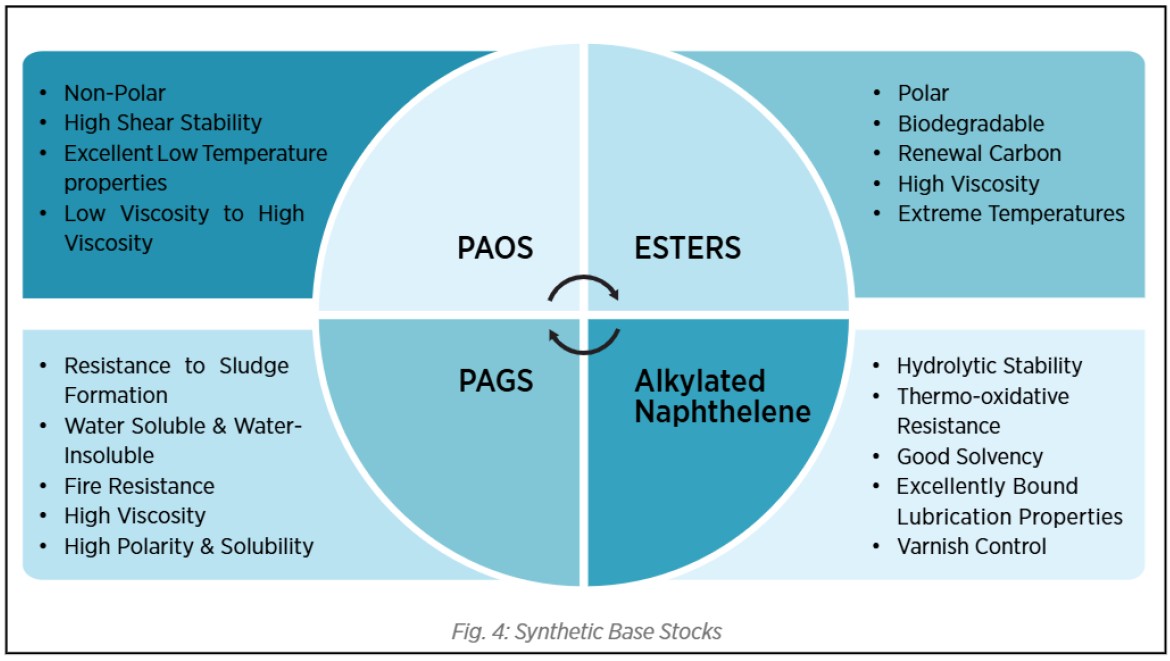
Exploring Group V Base Stocks: Versality Beyond Conventional Lubrication
API Group V base stocks are a diverse category of base oils that do not fall under the classifications of Groups I-IV as defined by the American Petroleum Institute (API). These base stocks include Esters (Synthetic Esters as well as Natural Esters), Polyalkylene Glycols (PAGs), Polyisobutenes (PIBs ), Alkylated Naphthalene (AN), Silicone oils and other specialty synthetics. They offer unique performance benefits, including superior thermal stability, biodegradability, and enhanced lubricity, making them suitable for high-performance and environmentally sensitive applications.
API Group V base stocks play a vital role in the evolving lubricant industry by offering superior performance, environmental benefits, and application versatility. As demand for synthetic and sustainable lubricants grows, these base stocks will continue to drive innovation and development in lubrication technology. Their future will be shaped by advancements in additive chemistry, evolving industry regulations, and new market opportunities in electric vehicles and high-performance applications.
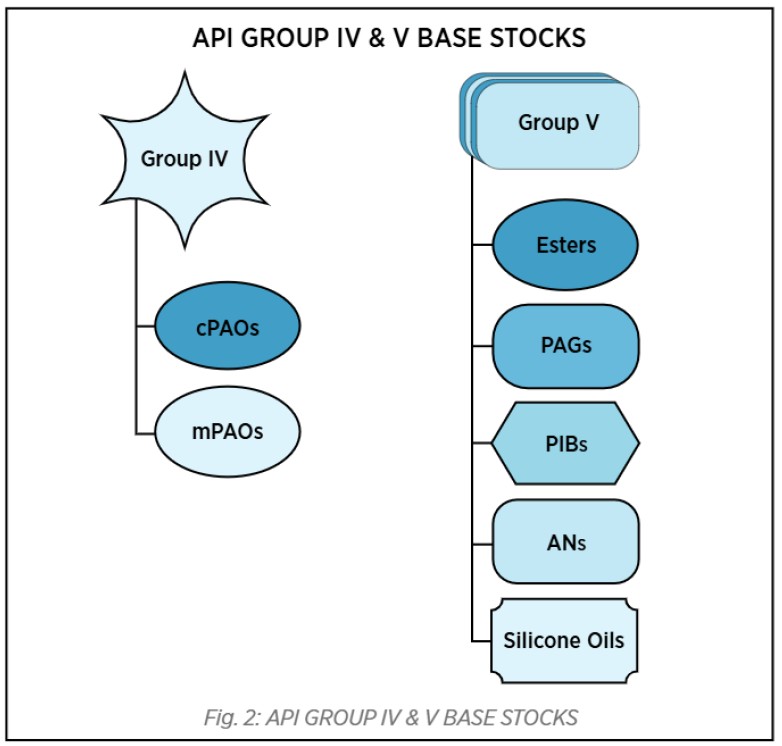
Let’s explore some of the key base stocks of this group in brief-
Polyalkylene Glycols (PAGS) – A Versatile Synthetic Base Stock
Polyalkylene Glycols (PAGs) belong to the API Group V base oil category and are distinguished by their excellent lubricity, outstanding thermal stability, and minimal sludge formation. Unlike conventional mineral oils, PAGs can be either water-soluble or water-insoluble, allowing for versatility across various industrial applications.
Let’s understand some of the notable Properties and Benefits of PAGs as hereunder-
- Exceptional Thermal Stability – Resistant to oxidation and thermal breakdown, ensuring extended service life
- High Viscosity Index – Maintains stable viscosity across fluctuating temperatures
- Minimal Sludge Formation – Helps keep systems clean, reducing maintenance needs
- Fire Safety – Certain PAG formulations possess self-extinguishing characteristics, making them suitable for fire-resistant fluids
- Environmental Compliance – Many PAGs are biodegradable, supporting eco-friendly lubrication solution
- Superior Lubricity – Enhances wear protection and minimizes friction in demanding applications
Industrial and Automotive Uses:
- Compressor Oils – Preferred in refrigeration, air, and gas compression systems due to their oxidation resistance and low volatility
- Fire-Resistant Hydraulic Fluids – Ideal for industrial setups where non-flammable lubricants are required
- Gear Lubricants – Provides strong film strength and high load-bearing capacity in gear applications
- Metalworking Fluids – Applied in machining for cooling and lubrication efficiency
- Electric Vehicle (EV) Applications – Utilized in transmission fluids due to their dielectric nature
With growing demand for high-performance and environmentally friendly lubricants, PAGs are expected to play an increasingly significant role in the future of synthetic lubrication technology.
Polyisobutylenes (PIBS) – A Versatile Viscosity Modifier
Polyisobutylenes (PIBs) are specialty base stocks categorized under API Group V, valued for their ability to enhance viscosity, resist oxidation, and improve tackiness. These polymers serve as critical components in lubricant formulations, optimizing film strength, reducing evaporation losses, and maintaining stability across a range of temperatures. Available in various molecular weight grades, PIBs offer versatility in applications spanning industrial lubricants, fuel additives, and sealants.
Let’s delve into some of their distinctive features and performance benefits as hereunder-
- Effective Viscosity Boosting – Contributes to improved lubricant film integrity and load-bearing capacity
- Superior Oxidation and Heat Resistance – Enhances lubricant durability under extreme conditions
- Low Volatility – Minimizes evaporation losses, making PIBs ideal for high-temperature environments
- Adhesion & Tackiness – Improves lubricant cling in applications such as chain oils and wire rope lubricants
- Outstanding Shear Stability – Maintains viscosity even under high mechanical stress, ensuring prolonged lubrication
Common Applications
- Engine & Gear Oils – Functions as a viscosity modifier, improving wear protection and overall lubricant stability
- Two-Stroke Engine Oils – Helps control deposits and lowers exhaust smoke emissions
- Adhesive & Tackified Lubricants – Essential for chain oils, wire rope lubricants, and specialized industrial greases
- Fuel Additives – Acts as a dispersant in gasoline and diesel fuels to minimize deposit formation
- Sealants & Grease Formulations – Enhances water resistance and sealing efficiency in industrial applications
With the increasing demand for high-performance and environmentally friendly lubricants, PIBs continue to play a crucial role in modern formulations by providing superior viscosity control and film strength.
Alkylated Naphthalene (AN) – A High-Performance Base Stock
Alkylated Naphthalenes (ANs) are synthetic base stocks categorized under API Group V, renowned for their remarkable resistance to oxidation and exceptional thermal stability. They seamlessly blend with various base stocks, enhancing lubricant performance under extreme conditions. They act as a high-performance alternative to traditional mineral oils and are often used as a co-base stock or additive to enhance lubricant durability in extreme conditions. ANs exhibit excellent solvency and lubricity, akin to esters, yet they provide superior resistance to hydrolytic degradation.
This category of synthetic fluids exhibits exceptional thermo-oxidative and hydrolytic stability, along with low volatility and excellent solubility characteristics. Additionally, recent studies on Electrohydrodynamic (EHD) film thickness and pressure-viscosity coefficients highlight their strong performance, making them a viable alternative to synthetic esters.
Let’s have a look at some of the key attributes and advantages along with application areas of Alkylated Naphthalene as hereunder-
Key Attributes and Advantages:
- Exceptional Oxidation Stability – Extends lubricant lifespan by preventing sludge accumulation due to enhanced resistance to sludge formation
- Robust Thermal Stability – Maintains performance integrity under high-temperature operations
- Effective Solvency – Enhances additive solubility as well as good compatibility with various lubricant formulations helping in optimizing lubricant formulations
- Wear and Friction Mitigation – Enhances equipment efficiency and longevity due to improved lubrication efficiency
- Reduced Volatility – Minimizes oil consumption in high temperature applications
Some of the application areas of Alkylated Naphthalene can be-
- Industrial and Automotive Lubricants – Integral in formulating engine oils, gear oils, and turbine oils for improved durability
- High-Temperature Environments – Ideal candidate for compressor oils, thermal transfer fluids, and high-temperature chain oils
- Greases – Boosts oxidative stability and extends the service life of high-performance greases
- Synthetic Lubricant Formulations – Often combined with PAOs and esters to achieve desired performance characteristics. In some of the formulation/s it even replaces esters
- Glass Molding Fluids – Preferred for their exceptional thermal and oxidative resilience
As the demand for high-performance lubricants continues to grow, Alkylated Naphthalenes (ANs) are emerging as a preferred base stock. Their excellent balance of oxidative stability, additive compatibility, and thermal efficiency makes them an attractive choice for lubricant manufacturers.
Esters – High-Performance Synthetic Base Stocks
Esters are one of the most widely used API Group V base stocks, known for their outstanding thermal stability, lubricity, and biodegradability. Esters can be synthetic as well as Natural and they are derived from the reaction of acids and alcohols. Therefore, Esters can be designed in various ways selecting the right acid/s and alcohol/s and creating molecular structures that offer superior performance compared to conventional base oils. Esters are commonly classified into Monoesters (MOE), Di-esters (DIE), Polyol esters (POEs), Neopolyol Esters (NPE) and Complex esters (CXE), each designed as per requirements for specific lubrication application/s.
Let’s study some of the key properties and advantages of Esters-
- High Thermal and Oxidation Stability – Enables operation in extreme temperatures, extending lubricant life
- Superior Lubricity – Reduces friction and wear, enhancing component durability
- Excellent Solvency – Improves additive dispersion, ensuring optimal lubricant performance
- Low Volatility – Reduces oil loss and evaporation at high temperatures
- Lower Coking Propensity – Esters have low coking propensity, thereby, making them eligible for speciality applications in aviation sector
- High Viscosity Indices – Esters have higher Viscosity Indices, thereby finds employment in HVI hydraulic oils and other high-end lubricants
- Low Pour Points & Higher Flash Points – Esters demonstrate excellent extreme temperature properties both in lower zone and higher temperature zones
- Biodegradability and Renewability – Many esters are biodegradable, renewable, and widely used in formulations that comply with environmental regulations for eco-friendly lubricants
Esters – Types
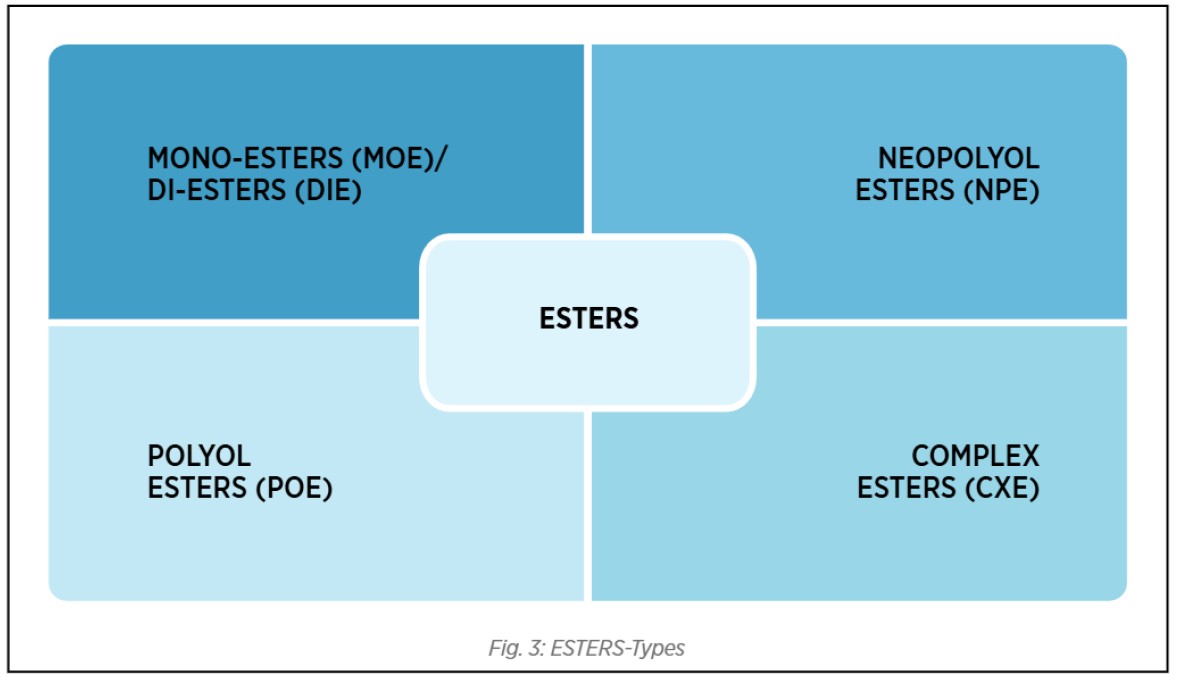
Let’s understand some of the unique application areas of the esters-
- Aviation and Aerospace Lubricants – As esters especially, synthetic esters can withstand extremes of temperatures and have high thermo-oxidative stability. Thereby making them unique base stocks for aviation and aerospace lubricants as most of the jet engine oils and turbine oils are formulated based on esters.
- Automotive and Racing Oils – Preferred in high-performance engine oils for superior wear protection.
- Biodegradable Hydraulic Fluids – Essential in environmentally sensitive applications like forestry and marine industries to protect the environment.
- Compressor and Refrigeration Oils – Offers excellent lubrication in high-pressure and low-temperature conditions.
- Metalworking Fluids and Greases – Enhances lubricity and stability in demanding industrial processes.
- Transformer Oils – Esters due to it’s unique combination of various properties like higher fire/flash points, biodegradability, excellent di-electric and thermos-oxidative properties, makes it most suitable candidate for transformer oils and readily acceptable in this industry.
- Refrigeration Oils – Another unique application area for Esters are refrigeration industry wherein POEs are compatible with Chlorine free refrigerants like HFCs, and Group I/II/III are not compatible. Therefore, for all industrial refrigeration application areas like chillers, cold-chains, cold storages, etc. using HFCs refrigerants, Esters are only the choice to Lubricant companies.
Due to their exceptional performance characteristics, esters continue to be a vital component in advanced lubricant formulations, offering sustainability and efficiency across various industries.
Synthetic Base Stock
Conclusion
The demand for synthetic base stocks is increasing, fuelled by stricter environmental regulations, advancements in automotive and industrial technologies, and the growing need for high-performance lubricants. Emerging markets—such as India, Southeast Asia, the Middle East, Africa, Latin America, and Eastern Europe—are at the forefront of this shift, offering substantial growth potential due to rapid industrial expansion, rising vehicle ownership, and expanding manufacturing sectors.
Some key growth drivers for synthetic base stocks include the shift towards Electric Vehicles (EVs), the industry’s focus on reducing maintenance and operating costs, and the need to minimize downtime in industries. These factors drive the adoption of synthetic lubricants formulated with these advanced base stocks. Moreover, evolving OEM specifications and the push for better fuel efficiency, extended oil drain intervals, and enhanced performance continue to propel the demand for synthetic base stocks.
Growing sustainability efforts and regulatory mandates are pushing the demand for environmentally friendly lubricants with a reduced carbon footprint, particularly those derived from renewable sources. This trend is driving greater adoption of advanced base stocks like Esters and PAGs, especially in applications where eco-compliance is a priority.
As industries and automotive sectors strive for greater efficiency and sustainability, synthetic lubricants have emerged as a crucial solution for energy conservation and performance enhancement. Unlike conventional mineral-based lubricants, synthetic base stocks offer superior lubrication, reduced friction, and enhanced thermal stability, contributing to significant energy savings across various sectors. Core industries such as mining, iron & steel, cement, power, and heavy engineering and others can significantly benefit from this transition. For example, a steel manufacturing plant utilizing synthetic gear oils in rolling mills could achieve energy savings of 5-8% while enhancing equipment uptime. Similar advantages extend across various industries, reinforcing the value of synthetic base stocks in optimizing performance and sustainability.
The transition from conventional to synthetic lubricants is no longer a luxury but a necessity for industries or rather it is now the need of the hour as today industries are aiming for higher energy efficiency and sustainability. With proven energy savings, extended service life, and reduced environmental impact, synthetic lubricants are a strategic investment for companies seeking long-term operational efficiency and cost reduction.
To fully harness the potential of synthetic base stocks in emerging markets, continued innovation and investment are essential. Local manufacturing capabilities, strategic partnerships, and advancements in feedstock technology will help address the cost and supply chain challenges. Collaboration among lubricant producers, OEMs, and policymakers will be key to accelerating adoption and driving the next generation of high-performance lubricants.
As the global lubricant industry evolves, synthetic base stocks will remain at the forefront of innovation, offering sustainable and high-performance solutions to meet the challenges of tomorrow’s markets.
About the Author
Vivek Gupta is a seasoned Mechanical Engineer with an MBA and over 25 years of expertise in the lubrication industry, specializing in Lubricant Additives and Base Stocks. His extensive experience covers Specialty and Super-Specialty Lubricants, as well as Automotive and Industrial Lubricants, with deep technical knowledge of Base Stocks, including API Group I, II, III, IV, and V (such as Esters, PAOs, PAGs, and ANs).
Currently, he serves as the National Key Accounts Manager at Coraplus India (a Vestcorp Holdings Group Company), where he plays a pivotal role in driving business growth. Throughout his career, he has held key positions in leading organizations, gaining invaluable insights into the evolving lubrication landscape.
For professional inquiries, you can reach Vivek Gupta at: [email protected] | [email protected]
